Understanding Total Lung Capacity (TLC) through Body Plethysmography
Total lung capacity (TLC) is a fundamental aspect of respiratory physiology, representing the maximum volume of air the lungs can hold after a full inhalation. Measuring TLC accurately is crucial for diagnosing, managing, and monitoring various pulmonary conditions. One of the most precise methods to determine TLC is body plethysmography, a technique that provides comprehensive insights into lung volumes and airway resistance.
Total Lung Capacity (TLC): An Overview
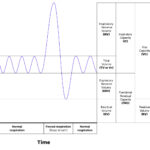
TLC encompasses all the air in the lungs, including the following volumes:
Tidal Volume (TV): The amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): The additional air that can be inhaled with maximum effort after a normal inhalation.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): The additional air that can be exhaled with maximum effort after a normal exhalation.
Residual Volume (RV): The air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation.
Mathematically, TLC is the sum of these volumes:
TLC=TV+IRV+ERV+RVTLC=TV+IRV+ERV+RV
Measuring TLC with Body Plethysmography
Body plethysmography is a sophisticated technique used to measure TLC and other lung volumes. It involves the use of a body plethysmograph, a sealed, airtight chamber in which the patient sits. The procedure exploits the principles of Boyle’s Law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at a constant temperature.
Procedure
Preparation: The patient is seated inside the body plethysmograph, which resembles a phone booth. They breathe through a mouthpiece connected to a flow sensor, while their nose is clipped to prevent air escape.
Measurement of Thoracic Gas Volume (TGV): The patient pants against a closed shutter, causing small pressure changes in the chamber and their lungs. These pressure changes are used to calculate the TGV, which closely approximates the RV.
Calculation of TLC: Once the TGV (or RV) is determined, other lung volumes measured through spirometry can be added to compute the TLC. For example, TLC can be found using the formula:
TLC=TGV+IRV+TVTLC=TGV+IRV+TV
Advantages of Body Plethysmography
Accuracy and Precision: Body plethysmography provides highly accurate measurements of lung volumes, including those that cannot be measured directly by spirometry alone, such as RV.
Non-Invasive and Comprehensive: The procedure is non-invasive and offers a comprehensive assessment of lung function, crucial for diagnosing obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
Detailed Airway Analysis: Besides lung volumes, plethysmography also measures airway resistance, helping in the assessment of conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Clinical Significance of TLC Measurement
Understanding and accurately measuring TLC has significant implications in clinical practice:
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Diseases
Abnormal TLC values can indicate various pulmonary conditions. Increased TLC may be seen in obstructive lung diseases like emphysema, while decreased TLC is often associated with restrictive lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis.
Monitoring Disease Progression
Regular measurement of TLC helps in monitoring the progression of chronic lung diseases and evaluating the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
Pre-Surgical Assessment
TLC measurements are essential in pre-operative evaluations to assess a patient’s respiratory reserve and predict potential complications.
Research and Development
TLC data contribute to respiratory research, enhancing the understanding of lung mechanics and aiding in the development of new treatments and interventions.
Conclusion
Body plethysmography stands out as a pivotal method for measuring total lung capacity, providing detailed and accurate lung volume assessments. This technique is indispensable for diagnosing and managing various respiratory conditions, offering insights that are crucial for effective clinical decision-making and patient care. As respiratory health continues to be a critical aspect of overall well-being, advanced tools like body plethysmography play an essential role in advancing our understanding and treatment of lung diseases.